Tactical fighter. Designed OKB-155 (Mikoyan Design Bureau and M.I.Gurevicha). Work on the fighter began in 1952. In the summer of 1953 the Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR, which were instructed to begin the development of aircraft designed for hypersonic speeds.
The OKB Mikoyan began work on the project E-1 fighter with swept wings and engine AM-11 design AA Mikulin. Due to the delay of the aircraft engine development project has been modified for installation of the engine AM-9B with a thrust of 3250 kg of the MiG-19 .
The new fighter was a cipher E-2, it is different from the E-1 aerodynamic ridges under the aft fuselage and the split slats. At the same time, work began on a version of the E-5 fighter with a delta wing and the same engine AM-11. For the same reason the project was changed to E-4 engine AM-9B with a thrust of 3250 kg.
The first prototype with swept wings E-2 (later named the MiG-23 - the first with this name) made its first flight 14 February 1955 ( Test Pilot G.K.Mosolov). The first prototype with a delta wing E-4 was built in 1955 and first flew on June 16, 1955 (test pilot G.A.Sedov). In tests, the E-4 showed the maximum speed of 1296 km / h while the C-1 on tests of the Sukhoi Design Bureau has exceeded 2000 km / h. In the process of finalizing the aircraft E-4 replaced the wing - instead of one large aerodynamic ridge located under the wing, installed three small over the wing, wing tips cut off. RD-9B was replaced by RD-9And.
The modified E-4 made its first flight September 5, 1956 (test pilot G.A.Sedov). Construction of a second prototype E-4 on the basis of the project E-5 was launched in 1955 by establishing a modified airplane wing overhead wind-swept ridges and 57 degrees. The plane was created by RD-11 (AM 11). E-5 prototype first flew on January 9, 1956 (test pilot V.A.Nefedov). During the tests the aircraft was officially named the MiG-21. At the end of 1957 it was stopped the development of the aircraft E-2 / MiG-23 with swept wings. Testing E-5 to be completed in May 1958 Total aircraft E-4 and E-5 conducted more than 100 missions and 98, respectively (all copies of the E-2 and E-2A made 250 flights).

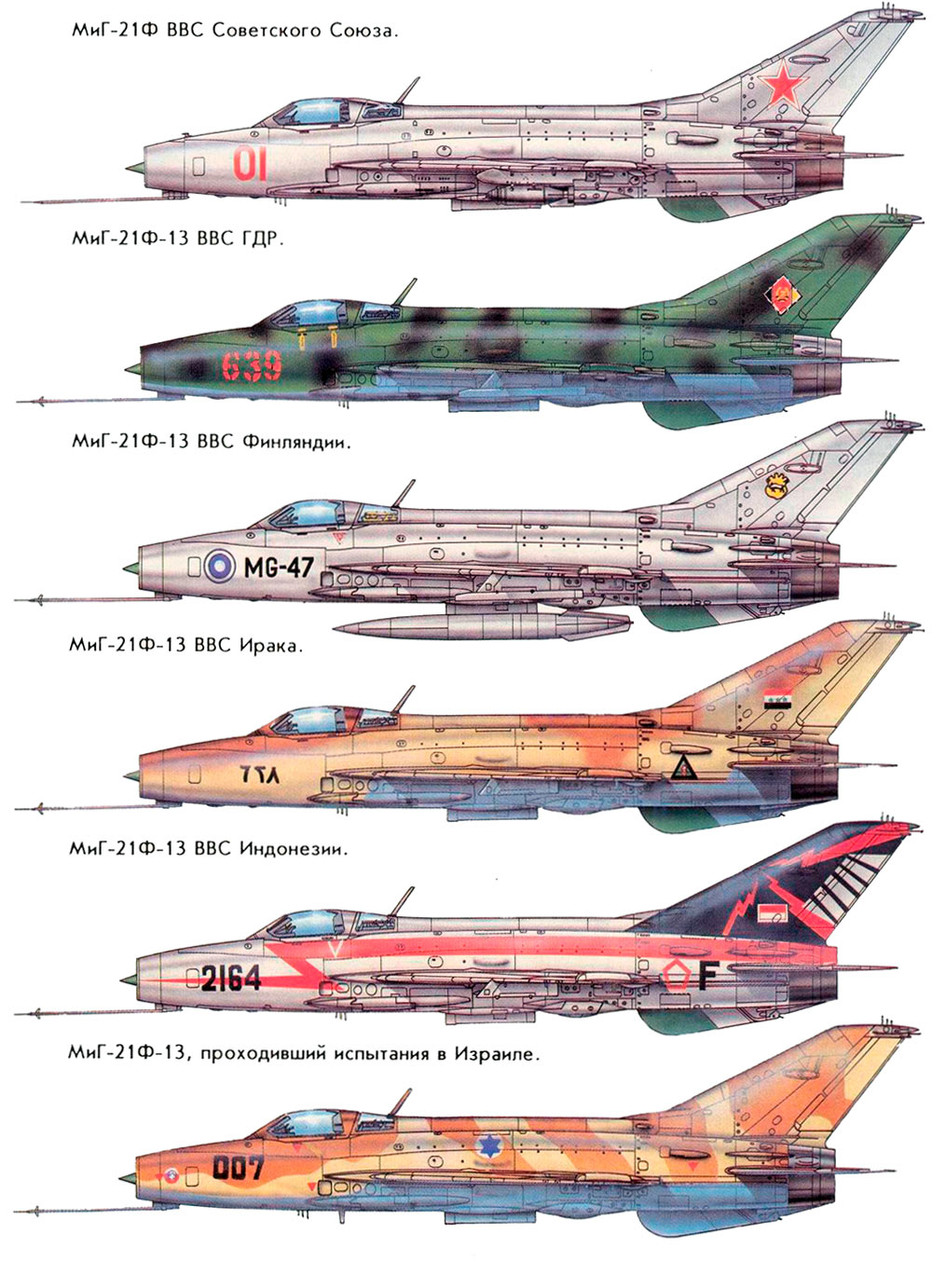
MiG-21F-13 board №84 "red" squadrons "aggressor" US Air Force. The aircraft was previously in the Indonesian Air Force. Aerodrome Tonopah, 1986 ( http://airwar.ru ).
Under the forced variation of the engine AM-11 - the product "37F" - was launched to provide an improved MiG-21 - E-6 aircraft. The first flight of the E-6-1 made May 20, 1958 (test pilot - V.A.Nefedov). The aircraft features a new engine and design improvements (see. Below). During the seventh flight of the E-6 (Test Pilot - V.A.Nefedov) after stopping the engine at an altitude of 18,000 m car crash landed, and the test pilot was killed. After this disaster from the plane E-6-2 has been removed electric control system, hydraulic and has been dubbed. Test three aircraft E-6 were in LII and mostly in Krasnovodsk in 1958-1959 GG Identified the main performance characteristics of the future MiG-21F.
USSR Council of Ministers Resolution №831-398 of 24 July 1958, the order №304 GKOT prescribed factory №21 (g.Gorky) start on the basis of small series of MiG-21 series production of the MiG-21F ( article "72", E-6) with an engine-11F P-300. The decree provides alterations in the MiG-21F and testing of two copies of the MiG-21 in the 4th quarter of 1959 is also the plant were ordered to cease production of the MiG-21 engine P-11-300 and secure the release of 12 MiG-21F. In the prototype of the MiG-21F / E-6 provides for the replacement of guns with HP-30 TKB-515, as well as the installation CD-30 radar and missiles "air-air".In 1958, production of the MiG-21F was deployed on №31 Tbilisi aircraft factory (in 1958 built the first 7 copies). Just a series of MiG-21F produced at the Moscow plant "Banner of Labor" (factory №30, now MiG, Moscow) in 1959 (released 30 copies.) And at the Gorky aircraft plant №21 (69 copies. In 1960 .). In 1960-1962 GG and in Moscow and Gorky serially produced MiG-21F-13. Serial production of the MiG-21F-13 for the Soviet Air Force in 1962, discontinued later aircraft modifications were made for export only.
The design - cantilever monoplane of normal aerodynamic configuration with a triangular plan tselnopovorotnym swept wing and stabilizer. The air intake - a supersonic multi-mode variable input section (due to the moving of the central body). The prototype E-6 (the future MiG-21F) differed from the E-5 / MiG-21 improved aerodynamics bow fyuzhelyazha, which established a new front with a fine cook lip and dvuhskachkovym cone. By increasing the speed of the aircraft air flow to the engine, to regulate the movement forward of the cone is not as smoothly as on the E-5, and the two races - for speeds 1,4-1,5M and 1.9M. In addition, several dropped down horizontal tail, have established a new standard equipment, improved the wing by holders rockets. System Rescue Crew: SK ejection system provides safe evacuation of the airplane at speeds up to 1100 km / h. The canopy opens upward and forward zazizaya pilot during ejection from the incoming air flow.
Engines : 1) E-5 (original project) - 1 x TRD AM-11 AA Mikulin development with a thrust at maximum capacity 3800 kg (afterburner - 5100 kg). 2) E-4 - TRD RD-9E (modification of the engine AM-9B) with a thrust in afterburner 3250 kg in 1956 to E-4 engine was replaced by RD-9And. 3) E-5 - TRD P-11 (AM-11 / RD-11 / R-11-300) with a thrust of 3800 kg, afterburner 5060/5100 kg (according to various sources). 4) E-6, the MiG-21F and MiG-21F-13 MiG-21U - turbojet P-11F-300 (product of "37F") with a thrust at maximum capacity 3880 kg (afterburner - 5740-5750 kg). Fuel - jet fuel T-1, T-2 and TS-1.
TTX fighter (the default data MiG-21F-13) crew - 1 person. (Educational-training modifications - 2 pers.)
| E-4 (1955) | E-5 (1956) MiG-21 | MiG-21F on the Resolution on the establishment of | E-6 / MiG-21F | MiG-21F-13 | MiG-21U | |
| Length | 15.76 m (with LDPE) | 13.46 m (without PVD) 15.76 m (with LDPE) | 12.18 m (without LDPE) | |||
| Wingspan | 7.749 m | 7.749 m | 7.154 m | 7.154 m | 7.65 m | |
| Swipe stabilizers | 3.5 m | |||||
| Height | 4.1 m | 4.1 m | 4.6 m | |||
| Wing area | 16.21 sq.m. | 22.95 sq.m. | 22.95 sq.m. | 22.95 sq.m. | ||
| Wing sweep | 57 degrees | 57 degrees | 57 degrees | 57 degrees | ||
| Sweep stabilizer | 55 degrees | 55 degrees | 55 degrees | 55 degrees | 55 degrees | |
| Sweep keel | 60 degrees | 60 degrees | 60 degrees | |||
| The base chassis | 4.81 m | |||||
| Track chassis | 2.69 m | |||||
| Maximum Takeoff Weight | 8376 kg (with 2 x FAB-500) | 8386 kg (with 2 X-FAB 500) 8620 kg | 9000 kg | |||
| Take-off weight is normal | 4443 kg | 6850 kg 7320 kg (with 1 x 490 liter drop tanks) | 7100 kg 7570 kg (with 1 x 490 liter drop tanks) | 7800 kg | ||
| Empty weight | 3500 kg? | 4819 kg | 4871-4980 kg | |||
| The mass of fuel | 2280 l / 1790 kg | 2280 l / 1790 kg (Head. №№ to 74,210,701 of 74,210,814) in 2470 l / 2115 kg | 2350 L / 1950 kg | |||
| Maximum speed (at an altitude) | 1296 km / h | 1970 km / h (18000 m) | 2300-2500 km / h | 1,100 km / h (at the ground) 2100 km / h / 1.97M (15,300 m) 2.05M - the speed limit | 1150 km / h (at the ground) 2175 km / h (altitude) | 1150 km / h (at the ground) 2175 km / h (altitude) |
| The maximum permissible speed (with missiles R-3S and without PTB) | 1,100 km / h (5000 m) 2100 km / h (12,500 m) | 1,100 km / h (5000 m) 2175 km / h (12,500 m) | ||||
| Cruising speed | 930 km / h (11,000 m) | |||||
| Speed landing | 260-270 km / h | |||||
| Acceleration | acceleration from 1.24M to 1.97M - 160 seconds | |||||
| Rate of climb | the height of 5000 meters in 96 | the height of 5000 meters in 96 | 20,000 m in height from 480-600 | 130 m / s height of 18,500 meters in 450 meters in height 20700 505 (E-6) | 142 m / s, the height of 10,000 meters in 192; height of 19,000 meters in 810 (missile); | |
| Ceiling practical | 16400 m | 17650 m | 21000-22000 m | 14500 m (E-6, the static ceiling without afterburner) 20700 m (E-6) | 19000 m | 18300 m |
| Range | 1120 km | 1330 km | 1,400 km 2,000 km (with the PTB) | 1520 km (without PTB) 1800 km (1 PTB) | 1,300 km (without PTB) 1580 km (1 PTB and missiles) 1670 km (Ferry) | 1210 km (without PTB) 1460 km (Ferry) |
| Maximum operating overload | 7 G | 7 G | ||||
| Acceleration from a speed of 600 km / h up to 1100 km / h | 28 | |||||
| Flight duration | 1.5 hours 2.25 hours (PTB) | 2-2,03 hours (PTB) | ||||
| Run | 730 m | less than 450 m | 800-900 m | 800-900 m | 800-900 m | |
| Mileage | 890 m | 450 m (with brake parachute) 850 m | 380-420 m (with brake parachute) 800-900 m |
Armament :
| E-6 / MiG-21F | MiG-21F-13 | |
| Artillery built | 2 x 30 mm cannon NR-30 (30 rounds of ammunition). Decree on the development of the MiG-21F / E-6 planned replacement cannons NR-30 on gun TKB-515. | 1 x 30 mm gun HP-30 (right in the fuselage) with 30 ammunition rounds (later increased to 60 rounds) |
| Missiles "air-air" (optional) | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 unit NUR UB-16-57U missile C-5M (ARS-57M) "air-air" Later: 2 missiles RS-2U / RS-2US complex K-5M (AA 1) 2 missiles R-3Scomplex K-13 (AA-2) the trigger AAP-13 | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 unit NUR UB-16-57U missile C-5M (ARS-57M) "air-to-air" missile 2 P-3C complex K-13 (AA-2), the trigger APU-13 later: 2 missiles RS-2U / RS-2UScomplex K-5M (AA-1) |
| Missiles "air-surface" | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 unit NUR UB-16-57U with rocketsor C-5K (CARS 57) 2 unit NUR Oro 57K NUR 2 C-24 (APC-240) | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 unit NUR UB-16-57U missile S-5K (CARS 57) 2 unit NUR Oro 57K NUR 2 C-24 (APC-240) |
| Bombs | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 bombs 50-500 kg (for holders D3-57) 2 tank incendiary ST-360 | 2 hardpoints under the wing of (options): 2 bombs 50-500 kg (for holders D3-57) 2 tank incendiary ST-360 |
| Suspended fuel tanks | In the suspension assembly can be installed under the fuselage of the PTB 490 liters | In the suspension assembly can be installed under the fuselage of the PTB 490 liters |
Equipment:
| E-5 (1956). | E-6 (1958) | MiG-21F, the MiG-21F-13 | |
| The sighting equipment / radar | DME TSS-1 coupled with the optical sight of TSA-5H | DME TSS-5 (MiG-21F) or SRD-5M "Quantum" HIGH FIX (MiG-21F-13) coupled with an optical sight ASP-SND (MiG-21F) or ASP-5ND (MiG-21F-13) provides start R-3S missiles at a distance of 1-7 km. Decree on the development of the MiG-21F / E-6 planned radar installation CD-30. | |
| Onboard computer | - | - | |
| IR-direction finder | - | - | |
| HUD | - | - | |
| Weapon control system | - | - | |
| The system of control of the aircraft | E-6-1 - hydraulic and electric, E-6-2 - after the accident E-6-1 Electric SA, which is overdue, has been removed and has been dubbed hydraulic | Autopilot CAP-2 (KAP-2K) Hydraulic SU (dubbed) | |
| Command guidance | - | - | |
| Navigation | Radio compasses ARK-5 Marker radio MRP-48P | Radio compasses ARK-5A (of the MiG-21F-13 - ARC-10) altimeter RV-3 (the MiG-21F-13 - RV-PA, a height of 600 m) Marker radio MCI-56m | |
| SRO | Defendant gosopoznavaniya "Barium-M" system radar warning receiver "Sirena-2" | Station SOD-57M, "chrome" and "chrome-nickel" (SRZO-2 on the MiG-21F-13), the SRO-2 system radar warning receiver "Sirena-2" | |
| Defense Complex REP | - | - | |
| Data transfer | - | - | |
| Stations | VHF RSIU-4 | VHF RSIU 5B (P-802B) | |
| Other avionics | - | - | |
| Refueling | - | - | |
| Other | Instead of landing lights on the MiG-21F-13 can be mounted camera AFA-39 |
Modifications :
- E-4 - the first prototype of the MiG-21, with a delta wing, built in 1955, the first flight - June 16, 1955 (test pilot - G.A.Sedov). The plane had a number of shortcomings in the tests did not go to design specifications and has been finalized. E-4 with the cut off wing tips and RD-9And first flew on September 2, 1956 (test pilot G.A.Sedov);
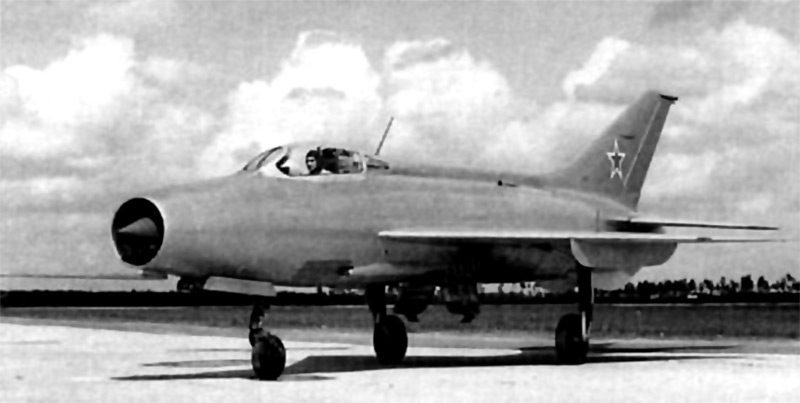

An experienced fighter E-4 with the engine RD-9B and wing with two large crests, 1955 ( http://aviadejavu.ru ). E-4 aircraft with modified krylomi RD-9And, 1956 ( http: // aviadejavu.ru ).
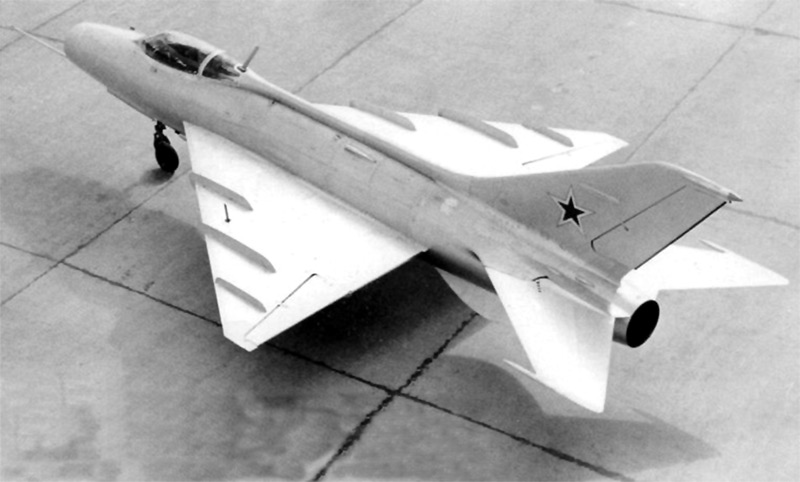


- E-5 / MiG-21 - the second prototype with a delta wing (first flight - January 9, 1956), eliminated the main shortcomings of the E-4, the name of the MiG-21 was awarded the car at the test stage, between May and July 1960 tested with ski gear.

An experienced fighter E-5, 1956 ( http://aviadejavu.ru ).
- E-5-2 - the second prototype of the E-5. From May to July 1960 the aircraft was tested operation with unpaved airfields with fixed landing gear with special skis. - MiG-21 - Serial E-5, produced in small series plant №21 (g.Gorky) 1958 - E 6 / E-6-1 - a modified version of the MiG-21 forced engine R-11F-300 and intake modifications, etc. Resolution of the Council of Ministers of the USSR №831-398 of 24 July 1958, the order №304 GKOT prescribed factory №21 (g.Gorky) start on the basis of small series of MiG-21 series production of the MiG-21F (article "72", E-6) with engine R-11F-300.
The decree provides alterations in the MiG-21F and testing of two copies of the MiG-21 in the 4th quarter of 1959 is also the plant were ordered to cease production of the MiG-21 engine P-11-300 and secure the release of 12 MiG-21F. In the prototype of the MiG-21F / E-6 provides for the replacement of guns with HP-30 TKB-515, as well as the installation CD-30 radar and missiles "air-to-air."
The first flight of the E-6-1 made May 20, 1958 (pilot - V.A.Nefedov). - E-6-2 - the second prototype fighter prototype of the MiG-21F (September 15, 1958, the pilot - KK .Kokkinaki). After 15 flights in LII plane was relocated in g.Krasnovodsk. Total program of factory tests aircraft made 46 flights, it has been replaced by three engines. In 1959 we finalized the airplane under suspension of R-3C at the ends of the wings - test changed the shape of the wing in the plan and about the middle of its sweep reduced from 57 degrees to 48 degrees.
The ends of the new wing have a greater slice them fastened launchers APU-13 missiles.Such a scheme suspension missiles tested in the Soviet Union 6-2 in the E-September 1960 to April 1961, however, assessed the results of the tests, the designers did not implement end the suspension of a series of rockets. - E-6-3 - the last pre-production prototype of the MiG -21F (1958). For the tests the aircraft entered the Krasnovodsk in December 1958 Tested application blocks NUR UB-16-57U.
Later remodeled in the E-66 (see below). - E-7-1 / MiG-21E - interceptor based on the MiG-21F, the first experimental prototype (1958). On the plane was set multifunction radar RP-21 (CD-30T). Due to the large diameter of the antenna changed the nose of the aircraft.
Armament missing, weapons - missiles K-13. Later, it finalized and adopted by both the MiG-21PF (see separate article). - MiG-21F (article "72") - the first production version of the MiG-21 - frontline fighter (1959), series production at the Moscow plant "Banner labor "(30 copies. in 1959) and at the Gorky aircraft plant (69 copies. in 1960); - E-6T / 6T-E-1 - prototype of the MiG-21F-13 (1959), in 1961 6T, the E-1 to set speed records converted LRE for the installation of V-21 turbojet engine and an advanced P-11F2-300 the first time in the cockpit appeared gargrot the fuel tank 170 liters. In 1959, it was tested several prototypes E-6T. - E-66 - a record machine, a converted aircraft E-6-3, October 31, 1959 set a speed record on the basis of 15-25 km - 2388 km / h (pilot - G.K.Mosolov) - MiG-21F-13 (product of "74") - the 13th, the second Large series MiG-21F (1960), increased the area of the keel, compared with the earlier MiG-21F on Gorky aircraft plant produced in 1960 - 132 copies., in 1961 - 272 copies., in 1962 - 202 copies.
Since 1960, as produced at the Moscow plant "Banner of Labor" for the Soviet Air Force production is completed in 1962, construction of the aircraft used aluminum alloys D16, B-25, M25T4, AK-4-1, magnesium alloy VM-65 1, steel and 30KhGSA 30HGSNA, fuselage skin thickness - 1.2 mm; central cone intake was recorded at different locations on Speeds up to 1.5 m, 1.5-1.9 m and over 1.9 M (at a lower speed of the cone is pulled into). MiG-21F-13 with some changes was made in Czechoslovakia and China (see. MiG-21. Chronology and export ).
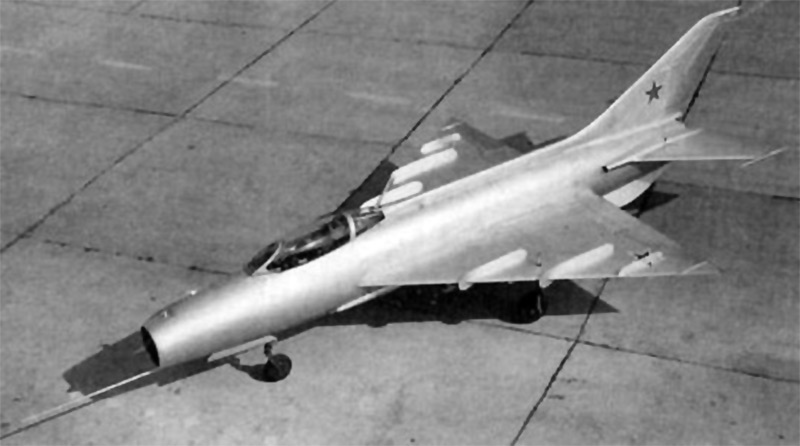
- E 7-2 / E 7-3 - the second and third prototype of MiG-21E, were tested as of mid-1960 E-7-2 first flight in January 1960 - E-6T-3 - an experienced fighter in 1960, is equipped with canards-destabilizer (PGO). Tested in 1960-1962 GG - E-6U-1 - prototype of the MiG-21U (first flight - October 17, 1960, the pilot - Ostapenko PM) - MiG-21U (the product "66" in the export performance - "66-400" - article "66" 400 series for India, as "66-600") - a training MiG-21F (mass production at the Tbilisi aircraft plant in 1962-1966 yy ., produced 180 copies.), optical sight ASP-5ND, katapulnye chair SC without braking parachute arming - 1 x 12.7 mm machine gun A-12.7, under the wing - up to 2 missiles P-3C; on the export of the aircraft was manufactured from 1964 to 1968 at the Moscow plant "Banner of Labor";
MiG-21U-600 Series was equipped with MiG-keel 21PFM and radar rangefinder SRD-5M; - E-66A - a record car based on the E-6 in the tank fairing and additional rocket engine, main series of records - April 28, 1961 - dynamic ceiling - 34714 m (the pilot - G.K.Mosolov). - E-60, E-60A and E-76 - a record of the machine; - E-6B - prototype based on the MiG-21F-13 (early tests - Summer 1963), improvement of landing at high angles of attack (16-18 deg.), testing SRM accelerators and ski gear.
Unlike mass-produced cars in the E-6B were installed nondisplacement landing flaps and tail support with shock absorber and roller located in the ventral fins. The system of blowing boundary layer (PCA) previously tested on one of the prototypes, has been disabled. The tests, conducted in July and August 1963 showed that when landing with a large angle of attack fighter has a small margin of longitudinal stability, greatly complicates review deteriorated steering technique and requires special training pilot.
As a result, such a landing was more complicated than using the PCA. - E-33 - record car based on the MiG-21U, the pilot N.Prohanova in May 1965 set a record altitude 24336 meters (dynamic ceiling) among women; in June 1965 aviatrix L.Zaytseva set a record height of level flight - 19020 m Some titles modifications cause some doubts (ever met in the press, but later not confirmed): MiG-21F-1 - MiG-21F 1 Series, according to some sources in 1962, a certain amount was supplied to India, the MiG-21F-5 - the MiG-21F of the fifth series, the MiG-21F-12 - Twelfth series of MiG-21F; MiG-21FA - MiG-21F two cannons NR-30; denote the modification of NATO notation: faceplate - E-2, E-2A; Fishbed-A - E-4, E-5; Fishbed-B - E-6; Fishbed-C - the MiG-21F; FISHBED-D - MiG-21PF; Fishbed-E - MiG-21PFS; Fishbed-F - MiG-21PFM; Fishbed-G - the MiG-21PD; Fishbed-H - the MiG-21P / RF; Fishbed-I - the MiG-21I Analogue 144; Fishbed-J - MiG-21MF; Fishbed-K - MiG-21SMT; Fishbed-L - the MiG-21bis; Fishbed-M -? intelligence, electronic warfare; Fishbed-N - MiG-21bisF (?); MONGOL-A - the MiG-21U; MONGOL-B - the MiG-21US / PA;
status and export - paper MiG-21. Chronology and exports .
Source : Aviation - astronautics. Issue 5/1995 Airshow - 1989 Khodynka. Moscow.Albov Q. How have fallen asleep in the Lord precursors "twenty-first". // Wings homeland. The N 4/1993 A. Bolotin, "Aviatika" MAI-890: a rich pedigree. // Wings homeland. N 5/1992 г. L. Bolshakov, Andryushkov A. MiG-21: aircraft survivor. // Red Star. 19.01.1993 Mr. C. Burdin, an obscure brother longevity. // Airplane. N 3/1994 г. Butovo P. Retirement is not going .// Wings homeland. N 5/1993 г. P. Butovo, as the old new. // Aviation and time. N 5/1995 г. Voivod SS, archive, 1990-1992 Military parade. N 1/1997 , Gordon E., V. Klimov, the MiG-21. Supplement to the "Wings of Motherland" N 1/1994 г. Grinyuk D. This fair colors ... // Wings homeland. N 2/1994 A. Dmitriev, the prospect of military aviation. // Independent Military Review. N 22/1997 Ilyin, first in the fourth generation. // Wings homeland. N 2-3 / 1992 Ilyin, seven is eight. // Wings homeland. N 12/1992, at 2, 6/1993 AP Kolesnikov, the MiG-21. // Technique-youth. The N 4/1992 Red Star. 01/04/1990 of Wings homeland. N 11/1991 г. B. Kulagin, the MiG-21. // Wings homeland. N 10/1975 г. S. Lukin, Be? // Aerohobbi. N 2/1992 Nikiforov, under the wing of the plane. // Airplane. The N 4/1994 SVT. Soviet military equipment. N 1/1996 Soviet armed forces.Tomsk. 1988 E. Stukanov, archive 1990 Technique-youth. N 7/1991 Egenburg C., Destiny. // Aerospace. N 2/1992 Beech E., Military aircrafts of the world. // Flight international. 21-27 august 1991. Enciclopaedia of Modern World Aircraft Armament. Christopher Chant.1988. England. Fluzeuge Hubschrauber und der NVA (von 1971 bis zur Gegenwart). Berlin. East Germany. Soviet Military Power - 1988. Washington. 1988. USA. World Armament & Disarmament 1975, 1976, 1977, 1979, 1981. SIPRI yearbook. Stocholm. Sweden.
No comments:
Post a Comment