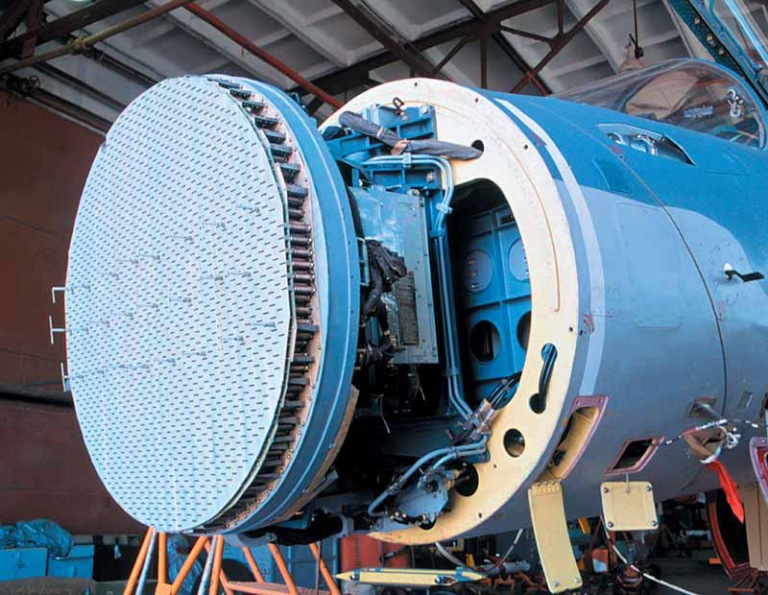

The BARS is the most advanced radar developed by Russian industry during the 1990s. It is unusual in being designed with a hybrid array arrangement, the receive path using very similar technology to US and EU AESAs, with similar sensitivity and sidelobe performance, but using a Travelling Wave Tube and backplane waveguide feed for the transmit direction, a technology closest to the B-1B and early Rafale EA radars.
As such the BARS is a transitional design sitting in between Passive ESAs (PESA) and contemporary AESAs. There is no doubt this design strategy reflected the unavailability to Russian designers of the Gallium Arsenide power transistors used in Western AESAs.
The baseline N011M radar uses a vertically polarised 0.9 metre diameter aperture hybrid phased array, with individual per element receive path low noise amplifiers delivering a noise figure cited at 3 dB, similar to an AESA. The antenna is constructed using phase shifter and receiver 'stick' modules, a similar technology to early US AESAs.
Three receiver channels are used, one presumably for sidelobe blanking and ECCM. The EGSP-6A transmitter uses a single Chelnok Travelling Wave Tube, available in variants with peak power ratings between 4 and 7 kiloWatts, and CW illumination at 1 kW. Cited detection range for a closing target (High PRF) is up to 76 NMI, for a receding target up to 50 NMI.
The phased array can electronically steer the mainlobe through +/-70 degrees in azimuth and +/-40 degrees in elevation. The whole array can be further steered mechanically. Polarisation can be switched by 90 degrees for surface search modes.
The BARS remains in production for the Indian and Malaysian Irkut built Su-30MKI/MKM variants. The radar is available with a range of TWT power ratings, this being the source of considerable confusion to observers who have not tracked this program since its inception. The result is a wide range of performance figures depending on the resulting Power Aperture Product. That the antenna has good power handling capability is evident in its adaptation for the Irbis E design.
Given the similarity between the Irbis E and BARS, existing BARS operators will over time effect block upgrades to convert their BARS inventories into the Irbis E configuration.
The N011M radar has been under flight testing since 1993, fitted to Su-27M (Su-35) prototype '712'. It employs the same level of technology as the now abandoned N014 radar which was to have equipped Mikoyan's MFI "fifth-generation" fighter and was initiated by Tamerlan Bekirbayev. The nose of the Su-30MKI was modified (compared the Su-27) to accommodate the fixed antenna array and more avionics boxes.
Note that the N011M is different from the N011: the N011 is mechanical scanning while the former is features a phased array antenna and is much more capable. The mechanical scan version equips the No 24 Sqn aircraft. "We can count the number of blades in the engine of the aircraft in sight (by the NO11M) and by that determine its type," NIIP claims.
The N011M can function both in air-to-air and air-to-land/sea mode simultaneusly while being tied into a high-precision laser-inertial / GPS navigation system. It is equipped with a modern digital weapons control system as well as anti-jamming features. The aircraft has an opto-electronic surveillance and targeting system which consists of a IR direction finder, laser rangefinder and helmet mounted sight system. The HMS allows the pilot to turn his head in a 90º field of view, lock on to a target and launch the much-feared R-73RDM2 missile.
In preliminary long range aiming, the targets (co-ordinates of which enter the navigation system) are locked on automatically, and the onboard locator is disengaged. The aircraft flies radio silent to the targets, and at a range close to the maximum one required for launching the weapons, the threat updating aids are engaged and the weapon is fired. In doing so, the attack time is minimal and the low-observable target approach increases the success of a mission greatly. The Su-30MKI can be fitted with an imaging IR navigation and attack equipment pod to provide night attacks against small-size ground targets.
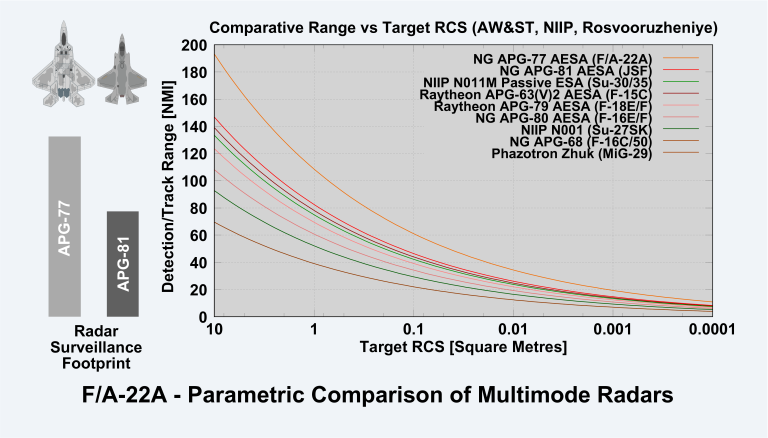
For aircraft N011M has a 350 km search range and a 200 km tracking range. The radar can track and engage 20 air targets and engage the 8 most threatening targets simultaneously. The forward hemisphere is ±90º in azimuth and ±55º in elevation. These targets can include cruise/ballistic missiles and even motionless helicopters. A MiG-21 for instance can be detected at a distance of up to 135 km. Design maximum search range for an F-16 target was 140-160km. A Bars' earlier variant, fitted with a five-kilowatt transmitter, proved to be capable of acquiring Su-27 fighters at a range of over 330 km. In comparison, the advanced Kopyo radar found in the latest MiG-21UPG can detect small drone targets at a range of 50 km.
Another radar meant for the Flanker family, Phazotron-NIIR’s Zhuk-MS radar has a range of 150-180km against a fighter and over 300km against a warship. N011M can withstand up to 5 percent transceiver loss without significant degredation in performance. Additionally the Su-30MKI can function as a 'mimi-AWACS' and can act as a director or command post for other aircraft. The target co-ordinates can be transferred automatically to atleast 4 other aircraft. This feature was first seen in the MiG-31 Foxhound, which is equipped with a Zaslon radar.
Radar Details ::
The forward facing NIIP NO11M Bars (Panther) is a powerful integrated passive electronically scanned phased array radar. The N011M is a digital multi-mode dual frequency band radar.
Features:
* The N011M can function both in air-to-air and air-to-land/sea mode simultaneusly while being tied into a high-precision laser-inertial or GPS navigation system. It is equipped with a modern digital weapons control system as well as anti-jamming features.
* For aircraft N011M has a 350 km search range and a maximum 200 km tracking range, and 60 km in the rear hemisphere. A MiG-21, for instance can be detected at a distance of up to 135 km. Design maximum search range for an F-16 target was 140–160 km.
* The radar can track 20 air targets and process engage the 8 most threatening targets simultaneously and attack 4 most dangerous simultaneously[3] These targets include from cruise missiles to even motionless helicopters.
* Irkuts press release on the Su-30 MKI Mk3.
* The Su-30MKI can function as a 'mini-AWACS' and can act as a director or command post for other aircraft. The target co-ordinates can be transferred automatically to at least 4 other aircraft.
* The radar can detect ground targets such as tanks at 40- 50 km.
* The N011M is claimed to detect large sea targets at a distance up to 400 km, and small sized ones at a distance of 120 km.
When integrated with the Brahmos Missile, the Su-30MKI could become a formidable anti-shipping platform.
Future upgrades:
* Future upgrade plans include new gimbals for the antenna mount to increase the field of view to about 90-100 degrees to both sides. New software will enable a Doppler-sharpening mode and the capability to engage up to eight air targets simultaneously.
* By 2010, when the first totally-built Su-30MKI will roll out from HAL, it could be equipped with a new phased array radar called the Irbis (Snow Leopard), which will replace the N011M Bars. These reports are yet to be confirmed by the Indian Air Force or official sources. The Irbis has been widely misreported to be an active phased array.
It is not. NIIP in Vzlet, 2006 (a journal edited by noted aviation journalist A. Fomin) details the Irbis as a high power Passive electronically scanned array, built using the experience of the Bars project.
However, it will have a lighter antenna derived from the NIIP Osa (Wasp) radar, new servos to rotate the antenna in both axes, with a greater field of regard (adding up to a total of 100 degrees), and an entirely new architecture with dual travelling wave tubes, giving a range of 400 km against a 3 meter square target (RCS). Using new high speed computers, the Irbis will be able to track 30 targets and engage 8. It will also be KS-172 capable.
FAQs :
Q1. WHY N-011M BARS RADAR USED IN Su-30MKI CONSIDERED TO BE DIFFERENT FROM OTHER PESA SYSTEM??
ANS- It is developed by Tikhomirov, a Passive Electrical Scanned Array (PESA) radar, thats what generally said. But looking at its scanning pattern I’ll say it’s more of a hybrid system that integrates the advantages of Mechanically Scanned Array and PESA system. Unlike other PESA system it doesn’t use same receiver amplifier for each TRM module, rather it has separate system like AESA. But in case of signal transmitting it uses single Oscillator of fixed freq…So you can say it’s a transition from common PESA system to AESA system.
Q2. IS IT A X-BAND OR L-BAND SYSTEM ??
ANS-Yes it is a X-band radar of 8-12GHz freq. As i already told you, it’s a hybrid system, so It incorporates the L-band, 1-2GHz IFF (Identification of Friend-or-Foe) system to improve the performance, and also an
N011-0M mechanically steered antenna system.
Q3. ANYTHING ABOUT POWER O/P, FREQ. BAND, SCAN / COVERAGE ??
ANS- It can scan upto +/-70 degree in azimuth and +/- 45 degree in vertical axis, also it can be mechanically steered to +/-55 degree off bore-sight, thus giving the pilot a full +/-100 degree off bore-sight forward hemispherical coverage with 3dB noise figure same as an AESAR. It has 3 Indian made Ts-200 processor of 28GHZ speed with digital processing system and can perform 70million operation per second. Both static and flash memory are of 16MB size. The average power o/p each channel receiver is 1.2kw and 1kw illuminator for radar homing missile…so sum of all 3 channel receiver and target designator has power o/p of 4-5 kw.
Q4. GREAT AND WHAT DO YOU MEAN BY MULTI-MODE RADAR AND HEY YOU’VE NOT MENTIONED THE RANGE EITHER ??
ANS- Air-Air mode: 15 tracked and 4 engaged simultaneously, 400Km search range, 200km track range, 60km rear tracking. Also in Air-Air mode it can do a Raid assesment and NTCR.
Air-Ground/Maritime strike: 15 tracked, 2 engaged, for tanks it has detection range of 60km and for Naval ships or destroyers 90-120km. Features include Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging(SAR), Doppler beam sharpening, real beam mapping and Ground/Maritime Moving Target Indicator(GMTI/MMTI). So it is perfectly suited for swing-role missions where you have no confirmation over the threats either they are ground threats or enemy air defence fighter. You can switch to any mode any time according to your mission requirements. And thats what make it Multi-mode system.
No comments:
Post a Comment